Net Worth Disparities Across Medical Specialties
The financial landscape for physicians reveals significant disparities in net worth across different specialties. While some specialists amass considerable wealth, others struggle with substantial debt, impacting career choices and healthcare access. This article explores the factors contributing to these disparities, their implications, and potential solutions.
The Widening Gap: A Comparative Analysis
A substantial difference exists in the net worth of physicians, depending heavily on their chosen specialty. Data, while not readily available for 2025 specifically, reveals consistent trends showing significant wealth accumulation in procedural specialties like plastic surgery, orthopedics, cardiology, and urology, compared to those in primary care fields such as family medicine, pediatrics, and internal medicine. This gap represents millions of dollars in accumulated wealth and highlights a considerable imbalance within the medical profession. Why this dramatic difference? Several factors are at play.
Key Factors Influencing Physician Net Worth
Multiple factors contribute to the wealth disparity among physicians. These include:
Specialty Choice (Procedural vs. Non-Procedural): Procedural specialties generate significantly higher income due to higher fees per procedure and potentially higher patient volume. The income potential in these specialties far surpasses that of primary care, which often involves lower reimbursement rates and higher patient loads relative to income. This difference directly impacts long-term wealth accumulation.
Gender and Racial Disparities: Persistent gender and racial inequities in medicine continue to influence physician earnings. Women and minority physicians are often underrepresented in high-paying specialties, compounding the existing financial imbalance. Further research is essential to fully understand and address the systemic causes of these disparities.
Student Loan Debt: The significant debt incurred during medical training disproportionately impacts primary care physicians. High levels of student loan debt hinder savings and investment, making wealth accumulation challenging, compounding the existing financial pressures. The substantial debt load often necessitates a more conservative approach to financial planning.
Geographic Location: The cost of living significantly impacts net worth. Physicians practicing in high-cost areas require higher incomes to maintain comparable lifestyles. This factor adds an additional layer of complexity to comparing net worth across different specialties and geographical locations.
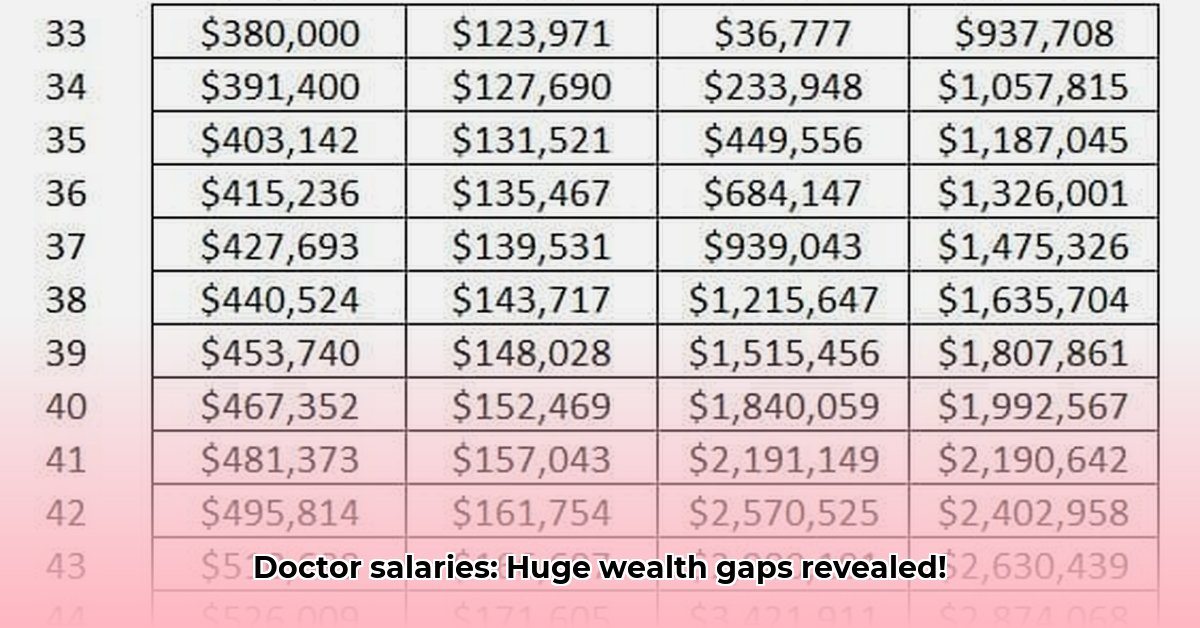
Illustrative Data: A Snapshot of Net Worth by Specialty
While precise 2025 data is limited, the following table illustrates the general trends based on available data reflecting previous years’ averages:
| Specialty | Estimated Average Net Worth (Illustrative) |
|---|---|
| Plastic Surgery | $5M+ |
| Orthopedic Surgery | $4M+ |
| Cardiology | $3.5M+ |
| Family Medicine | $1M+ |
| Pediatrics | $800K+ |
| Internal Medicine | $1M+ |
Note: These are broad estimates based on available data and individual physician wealth can vary significantly.
Implications for the Healthcare System
These wealth disparities have significant consequences. They can lead to:
Limited Access to Care: Fewer physicians may choose lower-paying but essential specialties, leading to shortages in primary care and underserved communities. This impacts access to quality healthcare for vulnerable populations.
Physician Burnout: The financial strain on primary care physicians can contribute to burnout, reducing the quality of care and potentially leading to workforce shortages. Sustainable financial models are critical to physician well-being and the delivery of quality healthcare.
Addressing the Issue: A Multi-Pronged Approach
Addressing physician wealth inequality requires a comprehensive strategy:
Fairer Compensation Models: Re-evaluating compensation structures to better reflect the value of primary care and other essential specialties is crucial.
Targeted Debt Relief Programs: Expanding and improving loan forgiveness programs for physicians serving in underserved areas can ease the financial burden.
Enhanced Financial Literacy Training: Providing physicians with financial literacy education can improve their ability to manage debt and build wealth.
Addressing Systemic Inequities: Proactive measures to address gender and racial disparities in medicine are essential to creating a more equitable system.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
The significant wealth gap among physicians underscores systemic issues within the healthcare system. Addressing these disparities requires a multi-faceted approach focusing on fair compensation, debt relief, financial literacy, and tackling systemic inequities. Further research is needed to fully understand and address these crucial issues. The goal is a sustainable healthcare system that values both patient care and physician well-being.